OPN
05. What is the flag in the hidden AP router behind default credentials?
Once we know your ESSID we can connect to the network, for that we create a “free.conf’ file to connect from bash using “wpa_supplicant”.
nano free.conf

wpa_supplicant: A daemon used to manage WPA/WPA2 authentication for Wi-Fi networks.-Dnl80211: Specifies the wireless driver backend.nl80211is the modern driver used for most Linux wireless devices.If
nl80211doesn't work, you might trywext(legacy driver).
-iwlan2: Specifies the wireless interface (wlan2in this case).You should check your actual interface name using
iwconfigorip link show.
-c free.conf: Specifies the configuration file (free.conf) containing network credentials and settings.

In another terminal as root:
sudo: Runs the command with superuser privileges.dhclient: A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) client that requests an IP address from a DHCP server.wlan2: The name of the wireless interface requesting the IP.-v: Enables verbose mode to display detailed output.


Once connected to the network and get IP with “dhclient” we can access the IP at IP 192.168.16.1 where we see a login where we can test default credentials such as admin/admin, accessing the admin panel where you can find the flag.


flag{680efaa62f7e953c24667285173711bc6bb6d3ff}
Alternate Method to connect



06. What is the flag on the AP router of the wifi-guest network?
For this challenge we have to access the wifi-guest network and bypass the captive portal. We can connect with the same method as in the previous challenge, but when we try to access the AP we find a captive portal that asks us for credentials. The AP is in the channel 6, so can monitor it first.

open.conf


In other terminal as sudo


To bypass this login we can use the MAC of a client connected to that network that we see with traffic, for that we can use airodump-ng again and impersonate one of those MAC.




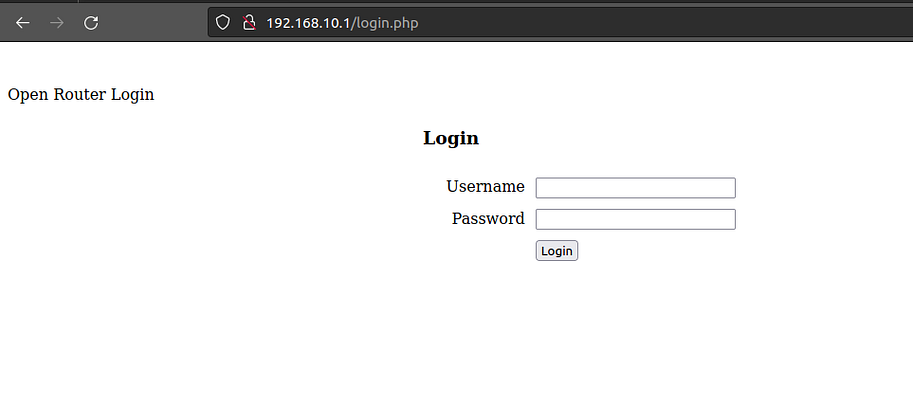
Once we have changed the mac with “macchanger” we connect again with “wpa_supplicant” and we can see that we can access the server login.

To obtain the login credentials we make a capture of “airodump-ng” saving the output with “-w” and after a while (3–5 min approx) we can see HTTP requests in the “.cap” file with “wireshark” in which there is a POST with username and password.


Form item: "Username" = "free2"
Form item: "Password" = "5LqwwccmTg6C39y"
flag{561004e3f4fd9fe640ecc0c411ac3129a4e08629}

Last updated