WPA3
Bruteforcing WPA3
In WPA3 networks it is still possible to brute force until the password is found, to do this we can use “wacker”.
Tab 1: Target Discovery
Identify the WPA3 network details.

Target SSID:
SweetB-WPA3BSSID:
02:00:00:00:02:00(Note: Use the specific MAC shown in your scan)Channel:
36Encryption: Look for WPA3 CCMP SAE.
Tab 2: The Wacker Attack
Wacker is a specialized tool that automates the SAE authentication loop to test passwords.
Navigate to Tool:
cd /home/rogue1/opt/wacker/Command:
Flag Breakdown:
--wordlist: Path to your dictionary file.--interface: Use a managed interface (e.g.,wlan1), NOT a monitor mode interface, as Wacker interacts with thewpa_supplicantstack.--freq: The frequency in MHz (e.g., Channel 36 =5180).
Success: When the password is found, it will output:
Found the password: 'password1'.

WPS3 Downgrate attack
If a network with WPA3 SAE has a client configured for WPA2/WPA3 we can perform a downgrade against the client forcing it to connect to our RogueAP with WPA2 obtaining the handshake to crack it later, as in the case of wifi-offices. In this case we can see that the AP uses SAE and PSK, so maybe the clients accept PSK too. We can get this information in the airodump-ng “.csv” file.


hostapd-sae.conf
This is a Hostapd configuration file used to set up a fake access point (AP) for penetration testing purposes. Here’s a breakdown of each line:
interface=wlan1→ Specifies that wlan1 is the wireless network interface to be used for hosting the fake AP.driver=nl80211→ Uses the nl80211 driver, which is common for modern Linux-based wireless devices.hw_mode=g→ Sets the 802.11g standard, which operates on the 2.4 GHz band and supports speeds up to 54 Mbps.channel=11→ Specifies Channel 11 (2462 MHz) for the AP.ssid=wifi-IT→ This is the SSID (Wi-Fi network name) that the AP will broadcast.mana_wpaout=hostapd-management.hccapx→ Captures WPA handshakes and saves them in the HCCAPX format, which is used for offline password cracking with Hashcat.wpa=2→ Configures WPA2 encryption (stronger than WPA1).wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK→ Uses Pre-Shared Key (PSK) authentication.wpa_pairwise=TKIP CCMP→ Supports both TKIP (legacy) and CCMP (AES-based, stronger encryption).wpa_passphrase=12345678→ Sets the Wi-Fi password to12345678.
What This Configuration Does
✅ Creates a fake Wi-Fi network named "wifi-IT" on channel 11 (2.462 GHz).
✅ Uses WPA2-PSK encryption with the password "12345678".
✅ Captures WPA handshakes in HCCAPX format for cracking later.
✅ Uses wlan1 interface with nl80211 driver.

We can check if the AP has MFP(802.11w) with Wireshark:
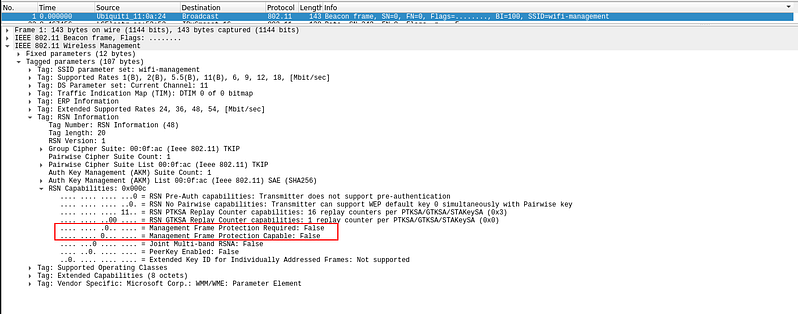
In this case 802.11w is disabled so we can deauth:

And you will be able to capture the handshake.

Save the hccapx to pcap
Export the 22000 hash mode from the pcap

Crack outside the VM or with a new version of hashcat.


Last updated